Difference between revisions of "Thync"
(sc.res.-the gap removed) |
(a correction) |
||
| (13 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
}} | }} | ||
| + | Thync is a small triangular-shaped head-mounted device that puts on the wearer's head. Headset stimulates and activates nerves. The user can either relax or energize. Brain neurons remain intact, the device releases only electrical impulses. In this way, Thync controls user´s mood.<ref name="TECHNEWSWORLD"/> | ||
| − | Thync is | + | Thync is wirelessly connected to the smartphone or tablet via Bluetooth (iOS or Android app). Users can control Thync by the official app where they can choose the length of the session. Also, they can adjust the strength of the stimulation there (each program follows a pattern of greater and lesser intensity, with cycles of peaks and valleys, but they can also manually raise or lower the overall strength).<ref name="GIZMAC">SHANKLIN, Will. Thync mood-changing wearable officially launches - we go hands on (again) [online]. [publ. 02.06.2015] All content copyright © Gizmag 2003 - 2015 [retr. 16.10.2015]. Available online at: http://www.gizmag.com/thync-hands-on-2/37820/</ref> |
| − | + | The manufacturer raised for this project $13.000.000 and started from October 2014.<ref name="TECHNEWSWORLD"/> From 02.06.2015 is the device already publicly available and its price is 299$ (7 245,37 CZK to the 22.9.2016).<ref name="Thync Launches"/> | |
| − | + | == Main Characteristics == | |
| − | + | Thync releases the low-level electrical pulses to the nerves in the various regions of brain. The manufacturers claim that by the stimulation of different regions, the change of mood appears. Namely, they claim that human mood is influenced by sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. The former is linked with "fight or flight" response and lead to increase of stress, while the latter is associated with relaxation. They argue that their device could increase the state of engergizing or the state of calmness, through stimulation of different regions of brain.<ref name="Science and Technology">THYNC.COM. Science/Technology [online]. Copyright 2015 Thync [retr. 20.10.2015]. Available online at: http://www.thync.com/science-and-technology</ref> | |
| − | == Main | ||
| − | Thync releases the low-level electrical pulses to the nerves in the regions of brain. | ||
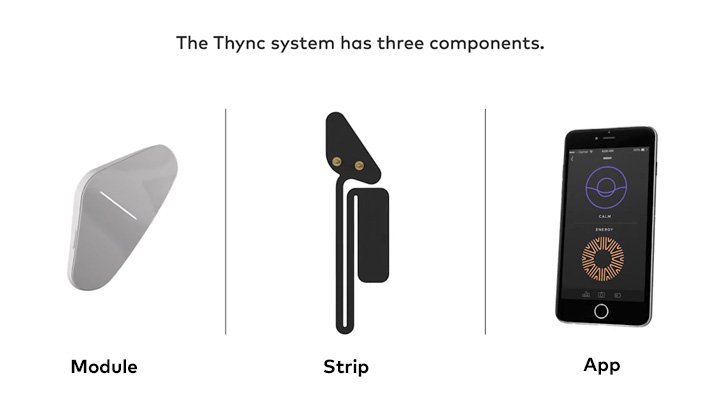
Thync system has three components: module, strips and app. Module placed on forehead and strips on the back of neck. Thync app controls calm or energy vibes via Bluetooth connecting to the smartphone.<ref name="Thync-Products">THYNC.COM. Products [online]. Copyright 2016 Thync [retr. 23.09.2016]. Available online at: http://www.thync.com/products</ref> | Thync system has three components: module, strips and app. Module placed on forehead and strips on the back of neck. Thync app controls calm or energy vibes via Bluetooth connecting to the smartphone.<ref name="Thync-Products">THYNC.COM. Products [online]. Copyright 2016 Thync [retr. 23.09.2016]. Available online at: http://www.thync.com/products</ref> | ||
| Line 46: | Line 45: | ||
[[File:Thync_Components.jpg|thumb|right|alt=Thync Components|Thync Components]] | [[File:Thync_Components.jpg|thumb|right|alt=Thync Components|Thync Components]] | ||
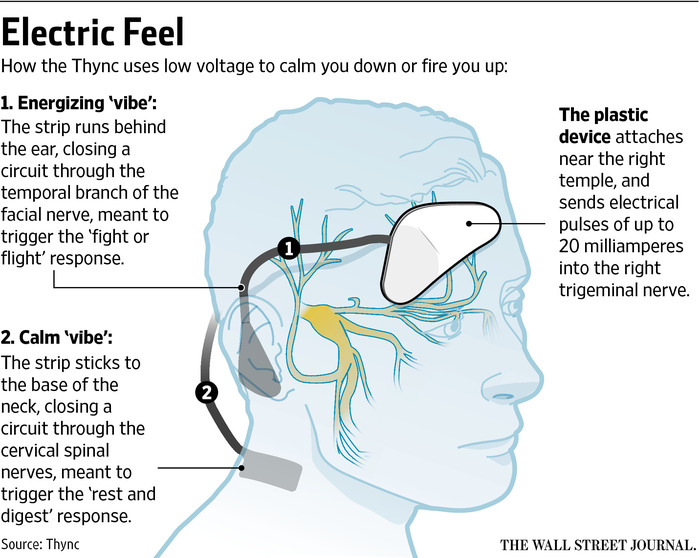
| − | The device is made of polycarbonate. The Strips and Liner are made of medical grade skin adhesives, | + | The device is made of polycarbonate. The Strips and Liner are made of medical grade skin adhesives, medical grade conductive adhesives, PET film, proprietary conductive inks (nickel free) and 10K gold plated brass snaps. <ref name="Thync-Products"/> |
| − | The dimension of the device is 1in X 2in X 0.5in (in cm: 2 | + | The dimension of the device is 1in X 2in X 0.5in (in cm: 2.54 x 5.08 x 1.27). The weight of the device is 18 grams. Thync is compatible with iPhone 5, 5s, 5c, 6 and 6 plus and with iOS 8 and higher. Battery Life is 4 to 6 vibes per charge and charge time takes approximately 2 hours via USB charging cable. Thync is wirelessly connected to the smartphone or tablet via Bluetooth (Bluetooth® 4.0 BLE). The other sensors are the singles colour LEDs that indicate power, charge states and current status. Syncing is manual and syncing range is 30 feet (9.15 m). Operating temperature is -4° to 113° F (-20°C to 45°C) and maximum operating altitude is 40,000 feet (12 200 m). Thync is not water resistant.<ref name="Thync-Products"/> |
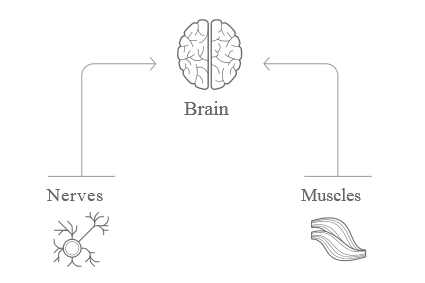
| − | With regard to the method, Thync uses neurosignaling to the change of mood. This method based on tDCS and TENS techniques | + | With regard to the method, Thync uses neurosignaling to the change of mood. This method based on [[Transcranial direct-current stimulation|tDCS]] and TENS techniques, which means that the small and constant direct current or the small pulses of direct current are delivered through skull.<ref name="Science and Technology"/> |
[[File:neurosignaling_block.png|thumb|right|alt=Neurosignaling technology that delivers signals to the brain through three neural pathways.|Neurosignaling technology that delivers signals to the brain through three neural pathways.]] | [[File:neurosignaling_block.png|thumb|right|alt=Neurosignaling technology that delivers signals to the brain through three neural pathways.|Neurosignaling technology that delivers signals to the brain through three neural pathways.]] | ||
=== Purpose === | === Purpose === | ||
Thync is a wearable device whose main purpose is the change of mood. Users can choose 2 modes: calm or energy. One session takes 15-20 minutes.<ref name="You Asked, We Answered"/> | Thync is a wearable device whose main purpose is the change of mood. Users can choose 2 modes: calm or energy. One session takes 15-20 minutes.<ref name="You Asked, We Answered"/> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
=== Company & People === | === Company & People === | ||
The Thync company was founded by Isy Goldwasser and Jamie Tyler in 2011 in Los Gatos, California. Their team is composed of these people:<ref name="About Us">THYNC.COM. About Us [online]. Copyright 2015 Thync [retr. 16.10.2015]. Available online at: http://www.thync.com/about</ref> | The Thync company was founded by Isy Goldwasser and Jamie Tyler in 2011 in Los Gatos, California. Their team is composed of these people:<ref name="About Us">THYNC.COM. About Us [online]. Copyright 2015 Thync [retr. 16.10.2015]. Available online at: http://www.thync.com/about</ref> | ||
| − | * Isy Goldwasser | + | * Isy Goldwasser: CEO and Founder |
| − | * Jamie Tyler Ph.D. | + | * Jamie Tyler Ph.D.: CSO and Founder (in March 2016 he was substituted for Sumon Pal) |
| − | * Sumon Pal Ph.D. | + | * Sumon Pal Ph.D.: Chief of Vibes |
| − | * Anil Thakur | + | * Anil Thakur: CTO |
| − | * Jason Egnal | + | * Jason Egnal: VP, Digital Marketing & Commercial Operations |
== Important Dates == | == Important Dates == | ||
| − | * 2011 | + | * 2011: Co-founding of Company Thync by experts in the fields of neurobiology, neuroscience and consumer electronics from institutions that include MIT, Harvard, and Stanford Universities.<ref name="About Us"/> |
| − | * October 2014 | + | * October 2014: Beginning of the project Thync.<ref name="About Us"/> |
| − | * June 2015 | + | * June 2015: Start selling the device Thync.<ref name="About Us"/> |
| − | * March 2016 | + | * March 2016: The company was experiencing the crisis and reduced his staff.<ref name="Bloomberg">HUET, Ellen. How Thync, Startup Behind Brain-Zapping Gadget, Almost Died [online]. [publ. 22.05.2016] ©2016 Bloomberg L.P. [retr. 29.11.2016]. Available online at: https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2016-05-23/how-thync-startup-behind-brain-zapping-gadget-almost-died</ref> |
| − | * April 2016 | + | * April 2016: The company put all of its assets up for auction, fortunately, Thync gained a new investor and therefore it was able to buy up its assets back.<ref name="Bloomberg"/> |
| − | * | + | * May 2016: The business has been moving forward.<ref name="Bloomberg"/> |
| + | |||
| + | == Enhancement/Therapy/Treatment == | ||
| + | |||
| + | In addition to the changes mood, it is deemed that it could help with sleep problems, reduce stress or the motivation to exercise. The manufacturers also believe that the people could reduce consumption of coffee, alcohol and drugs, as a result of introduction this device<ref name="Kyle Russell">RUSSELL, Kyle. Hands-On With Thync's Mood-Altering Headset [online]. [publ. 02.06.2015] TechCrunch. © 2013-2016 AOL Inc. [retr. 29.11.2016]. Available online at: https://techcrunch.com/2015/06/02/hands-on-with-thyncs-mood-altering-headset/#.jihnn2:JNRc</ref> The Thync company points out that their product Thync is not determined ''"to treat or diagnose any disease or medical condition"''.<ref name="Thync-Products"/> | ||
== Ethical Issues == | == Ethical Issues == | ||
| − | |||
| + | At the conferences that were summarizing named "Introduction to Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation in Neuropsychiatric Research" (2015) and that organized Harvard Medical School<ref name="HARVARD MEDICAL SCHOOL">HARVARD MEDICAL SCHOOL. Introduction to Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation in Neuropsychiatric Research [online]. Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, MA 02215, 2015 [retr. 9.11.2016]. Online available at: http://www.hms-cme.net/106409/</ref> were some ethical issues discussed. '''Alvaro Pascual-Leone''' criticized that the neurostimulation is using as off-label application and without examination or a full understanding of safety and efficacy implications.<ref name="Non-Invasive Neuromodulation">BAIN, Lisa. NORRIS, Sheena Posey. STROUND, Clare; Rapporteurs. Non-Invasive Neuromodulation of the Central Nervous System: Opportunities and Challenges [online]. United States : Forum on Neuroscience and Nervous System Disorders; Board on Health Sciences Policy; Institute of Medicine; The National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, 2015 (Summary Workshop). [retr. 20.10.2016]. ISBN 978-0-309-37618-1. Available online at: http://www.burke.org/docs/Research_Nina/iom-non-invasive-neuromodulation-ws.PDF</ref> '''Erik Parens''' focused on the non-physical harms. That means, ''"how a technology might do harm not to our bodies, but to us as human beings."'' He distinguishes 4 major concerns: inauthenticity, complicity, mechanization and inequality. Parens also criticizes that "''the distinction between treatment and enhancement is abstract and fuzzy"''.<ref name="Parens">PARENS, E. Why IOM Should Consider Broaching ‘Enhancement Concerns’ in the Context of Non-Invasive Brain Stimulation [online]. In Non-invasive Neuromodulation of the Central Nervous System: A Workshop. Washington DC : Institute of Medicine, of the National Academy of Sciences, March 3, 2015. [retr. 9.11.2016]. Available online at: https://www.nationalacademies.org/hmd/~/media/Files/Activity%20Files/Research/NeuroForum/2015-MAR-2/Presentations/Parens.pdf</ref> '''Martha Farah''' pointed to 4 overlapping categories: safety, efficacy, freedom and fairness.<ref name="Non-Invasive Neuromodulation"/> Furthermore, at the conference discussed the following topics: the distinction between treatment and enhancement, necessity of the further study of the long-term safety of neurostimulation, the impact of neurostimulation on the developing brain and the approval by FDA.<ref name="Non-Invasive Neuromodulation"/> | ||
| − | In the other study that was named ''"An ethical discussion of the use of transcranial direct current stimulation for cognitive enhancement in healthy individuals: a fictional case study"'' and that took place from the | + | |
| + | In the other study that was named ''"An ethical discussion of the use of transcranial direct current stimulation for cognitive enhancement in healthy individuals: a fictional case study"'' and that took place from the January till June 2014 in Rio de Janeiro, these ethical questions emerged:<ref name="Ethical Discussion">LAPENTA, Olivia M. VALASEK, Claudia A. BRUNONI, André R. BOGGIO, Paulo S. An ethical discussion of the use of transcranial direct current stimulation for cognitive enhancement in healthy individuals: a fictional case study [online]. Psychol. Neurosci. vol.7 no.2 Rio de Janeiro Jan./June 2014. [retr. 24.10.2016]. ISSN 1983-3288. Available online at: http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1983-32882014000200014</ref> | ||
''"(1) whether the modulation of "inner-self" characteristics, such as personality, impulsivity, and social behavior, is acceptable"'' | ''"(1) whether the modulation of "inner-self" characteristics, such as personality, impulsivity, and social behavior, is acceptable"'' | ||
| Line 90: | Line 92: | ||
== Health Risks == | == Health Risks == | ||
| + | [[File:Electric_Feel.jpg|thumb|right|alt=Electric Feel|Electric Feel]] | ||
According to the company, there have been no significant issues regarding Thync’s safety profile. It's known that many people engage in alcohol, drugs, and other activities due to stress, anxiety, and mood problems. Thync may allow for a safer way to alleviate these problems.<ref name="MEDTECH BOSTON">VAHABZADEH, Arshya. CHAN, Steven. Testing Thync: A Calming, Energizing Personal Brain Modulator [online]. [publ. 12.05.2015] Medtech ©2013-2016 Medical Networking, Inc. [retr. 8.11.2015]. Available online at: https://medtechboston.medstro.com/testing-thync-a-calming-energizing-personal-brain-modulator/</ref> | According to the company, there have been no significant issues regarding Thync’s safety profile. It's known that many people engage in alcohol, drugs, and other activities due to stress, anxiety, and mood problems. Thync may allow for a safer way to alleviate these problems.<ref name="MEDTECH BOSTON">VAHABZADEH, Arshya. CHAN, Steven. Testing Thync: A Calming, Energizing Personal Brain Modulator [online]. [publ. 12.05.2015] Medtech ©2013-2016 Medical Networking, Inc. [retr. 8.11.2015]. Available online at: https://medtechboston.medstro.com/testing-thync-a-calming-energizing-personal-brain-modulator/</ref> | ||
| − | Thync commented safety of their products on | + | Thync also commented safety of their products on their websites. They consider the Thync system as a safe and low-risk transdermal neurostimulation devices. But they also pointed that Thync is not intended to treat or diagnose any disease or medical condition.<ref name="Science and Technology"/> |
| − | As already stated above, the Thync uses TENS and | + | As already stated above, the Thync uses TENS and tDCS techniques. Risk of these methods is wrong placement of electrodes. Some people are right-handers, but the others are left-handers. Reversing the polarity can be dangerous and can lead to impairment of brain. At the best, it could mean ineffectiveness, in the worst, headache and brain disorders.<ref name="Mind Machines">MASLEN, Hannah. DOUGLAS, Thomas. KADOSH, Roi Cohen. LEVY, Neil. SAVULESCU, Julian. Mind Machines. University of Oxford, 2014. [retr. 10.12.2015]. Available online at: http://www.oxfordmartin.ox.ac.uk/downloads/briefings/Mind_Machines.pdf.</ref> The manufacturers of this device recommend that people suffering to Reflex Syncope should consult with their physician before purchasing a Thync System.”<ref name="Science and Technology"/> |
Thync company released on their website ''"Warnings, Precautions and Adverse Reaction"''<ref name="Thync-Products"/> too. | Thync company released on their website ''"Warnings, Precautions and Adverse Reaction"''<ref name="Thync-Products"/> too. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Public & Media Impact and Presentation == | == Public & Media Impact and Presentation == | ||
| − | Apart from the fact, that the Thync company has its own website, | + | Apart from the fact, that the Thync company has its own website, Facebook, Twitter and Youtube channel, there are the another web portals talking about Thync. |
| − | |||
Some people don´t believe that Thync works: | Some people don´t believe that Thync works: | ||
| Line 141: | Line 140: | ||
More detailed reviews are available for viewing below: | More detailed reviews are available for viewing below: | ||
| − | '''Andy Boxall''' assumed that he felt the effects of Thyncs. But he notes that ''"there’s a chance it won’t work for others."''<ref name="DIGITAL TRENDS">BOXALL, Andy. Thync Review [online]. [upd. 25.10.2016] Digital Trends, 2016 [retr. 19.10.2016]. Available online at: http://www.digitaltrends.com/fitness-apparel-reviews/thync-review/</ref> According to Thync, 80 percent of people will feel the effects. The next disadvantage are the ongoing costs. By them are meant the straps, which should be used only single time. | + | '''Andy Boxall''' assumed that he felt the effects of Thyncs. But he notes that ''"there’s a chance it won’t work for others."''<ref name="DIGITAL TRENDS">BOXALL, Andy. Thync Review [online]. [upd. 25.10.2016] Digital Trends, 2016 [retr. 19.10.2016]. Available online at: http://www.digitaltrends.com/fitness-apparel-reviews/thync-review/</ref> According to Thync, 80 percent of people will feel the effects. The next disadvantage are the ongoing costs. By them are meant the straps, which should be used only single time. A one pack (5 straps) costs 20$. If someone had used Thync every day, he would spent more than 80$ per month.<ref name="DIGITAL TRENDS"/> |
| − | '''John M. Grohol''', | + | '''John M. Grohol''', a psychologist, researcher and expert in mental health, is neutral about Thync. He tried Thync and described that felt an odd sensation but it wasn´t the sensation of calm. He wrote literally: ''"I didn’t feel an overwhelming sense of calm or euphoria as was suggested I might. But I did feel a sense of… something due to the device. You definitely feel it working. But it would be hard for me — in a single, short sitting — to say what that was."''<ref name= "GROHOL">GROHOL, J. What Thync Looks & Feels Like. In Psych Central. Copyright © 1995-2016 Psych Central [retr. 19.10.2016]. Available online at: http://psychcentral.com/blog/archives/2015/06/02/what-thync-looks-feels-like/</ref> |
| − | '''Natalie Salmanowitz''' has taken part in a Thync social event at the company’s offices at Runway Incubator. First, she felt the desired energy sensation. She said: ''"I am not an introvert, but I am also not a small talk enthusiast. Yet, from then on, I was hyper, extroverted, confident and mentally on point. Seems I was vibing."''Next day, she tried Thync at home and she felt a pain. About her experience, she speaks as follows: ''"The next day, I positioned the module the way I had been shown, and tapped start. I felt a familiar feeling, but not the pulsing buzz. Instead, the uncomfortable burning sensation was back. I tried dialling down the intensity and attaching new strips, but the pain persisted."''<ref name="SALMANOWITZ"/> She called by video chat with the support's team because of positioning process but the burning sensation was persisting. Natalia has visited the Thync's headquarters in Los Gatos. Thync's assistant had placed the module on her head but the burning sensation came back. Eventually, Thync's assistant confused that Natalie "deviated from the norm" and her skin was too sensitive for Thync. | + | '''Natalie Salmanowitz''' has taken part in a Thync social event at the company’s offices at Runway Incubator. First, she felt the desired energy sensation. She said: ''"I am not an introvert, but I am also not a small talk enthusiast. Yet, from then on, I was hyper, extroverted, confident and mentally on point. Seems I was vibing."''Next day, she tried Thync at home and she felt a pain. About her experience, she speaks as follows: ''"The next day, I positioned the module the way I had been shown, and tapped start. I felt a familiar feeling, but not the pulsing buzz. Instead, the uncomfortable burning sensation was back. I tried dialling down the intensity and attaching new strips, but the pain persisted."''<ref name="SALMANOWITZ"/> She called by video chat with the support's team because of positioning process but the burning sensation was persisting. Natalia has visited the Thync's headquarters in Los Gatos. Thync's assistant had placed the module on her head but the burning sensation came back. Eventually, Thync's assistant confused that Natalie "deviated from the norm" and her skin was too sensitive for Thync. Another colleague uttered his speculation: "The vibes depend on your current environment" in other words, may mean the placebo effect.<ref name="SALMANOWITZ"/> |
| − | '''Kyle Russell''' | + | '''Kyle Russell''' speaks about his experience with Thync on TechCrunch. He tried only the calm mode but he was satisfied with it: ''"While I was warned that Thync might not work the first time, a few minutes into my first session (using the Calm setting) I felt a wave of sluggishness pass over me. I had some difficulty putting words into a coherent question for Goldwasser, and felt a strong urge to take a nap that lasted until I got home. While I may have cranked the settings too high for my first go, the impression I got was that it would be great for falling asleep, not de-stressing at the office."''<ref name="Kyle Russell"/> |
| − | '''James Trew''' described his experience on the web Engadget | + | '''James Trew''' also described his experience on the web Engadget. He and his colleague Dan Cooper tried Thync at the same point and in the same hotel suit in Las Vegas. There are with them two neuroscientists of Thync (their names wasn't published). Each one of both felt different feeling because the one tried the calm mode and the other tried the energy mode. He only complained of it that the team of Thync has given no scientific explanation of neurosignaling method: ''"All I know for sure is that I enjoyed my experience. I liked it, and want to try it again. I don't know if this was placebo, a willingness for it to work or something else. I'm definitely not a morning person, and I left the briefing in a very different state to when I went in. I only wish the team were more explicit about the science, the stuff that's going on inside, and allowed us to reveal more about the product. Especially given the natural suspicion that many consumers have about "mood enhancing" devices, and even more so when they're propped up by incomplete insight into what's going on. Now that the energized feeling has faded, I'm left a little frustrated. Something only Thync can solve."''<ref name="James Trew">TREW, James. Thync's mood-changing wearable made me happy and frustrated [online]. [publ. 01.07.2015] Engadget. © 2016 AOL TECH(UK). [retr. 29.11.2016]. Available online at: https://www.engadget.com/2015/01/07/thync-mood-changing-wearable/</ref> |
| Line 159: | Line 158: | ||
The Thync neurosignaling product is protected by these patents: U.S. Patents 8,903,494<ref name="US Patent 08903494">GOLDWASSER, Isy and others. US 8,903,494 B2: Wearable Transdermal Electrical Stimulation Devices and Method of Using Them [online]. [publ. 02.12.2014] The Patent Reader ©2016 Noah K. Tilton [retr. 29.11.2016]. Available online at: https://patents.tilton.co/detail/ElecUtility/2014-12-02/08903494</ref>; US 9,002,458<ref name="US Patent 09002458">PAL, Sumon K. and others. US 9,002,458 B2: Transdermal Electrical Stimulation Devices for Modifying or Inducing Cognitive State [online]. [publ. 07.04.2015] The Patent Reader ©2016 Noah K. Tilton [retr. 29.11.2016]. Available online at: https://patents.tilton.co/detail/ElecUtility/2015-04-07/09002458</ref>; US 9,014,811<ref name="US Patent 09014811">PAL, Sumon K. and others. US 9,014,811 B2: Transdermal Electrical Stimulation Methods for Modifying or Inducing Cognitive State [online]. [publ. 21.04.2015] The Patent Reader ©2016 Noah K. Tilton [retr. 29.11.2016]. Available online at: https://patents.tilton.co/detail/ElecUtility/2015-04-21/09014811</ref>; and US 9,233,244<ref name="US Patent 09233244">PAL, Sumon K. and others. US 9,233,244 B2: Transdermal Electrical Stimulation Devices for Modifying or Inducing Cognitive State [online].[publ. 12.01.2016] The Patent Reader ©2016 Noah K. Tilton [retr. 29.11.2016]. Available online at: https://patents.tilton.co/detail/GMUtility/2016-01-12/09233244</ref>. The Chinese Utility Model Patent No. ZL201320760967.0.<ref name="patent">THYNC.COM: Patent [online]. Copyright ©2016 Thync Global Inc., U.S.A. [retr. 29.11.2016]. Available online at: http://www.thync.com/pat</ref> | The Thync neurosignaling product is protected by these patents: U.S. Patents 8,903,494<ref name="US Patent 08903494">GOLDWASSER, Isy and others. US 8,903,494 B2: Wearable Transdermal Electrical Stimulation Devices and Method of Using Them [online]. [publ. 02.12.2014] The Patent Reader ©2016 Noah K. Tilton [retr. 29.11.2016]. Available online at: https://patents.tilton.co/detail/ElecUtility/2014-12-02/08903494</ref>; US 9,002,458<ref name="US Patent 09002458">PAL, Sumon K. and others. US 9,002,458 B2: Transdermal Electrical Stimulation Devices for Modifying or Inducing Cognitive State [online]. [publ. 07.04.2015] The Patent Reader ©2016 Noah K. Tilton [retr. 29.11.2016]. Available online at: https://patents.tilton.co/detail/ElecUtility/2015-04-07/09002458</ref>; US 9,014,811<ref name="US Patent 09014811">PAL, Sumon K. and others. US 9,014,811 B2: Transdermal Electrical Stimulation Methods for Modifying or Inducing Cognitive State [online]. [publ. 21.04.2015] The Patent Reader ©2016 Noah K. Tilton [retr. 29.11.2016]. Available online at: https://patents.tilton.co/detail/ElecUtility/2015-04-21/09014811</ref>; and US 9,233,244<ref name="US Patent 09233244">PAL, Sumon K. and others. US 9,233,244 B2: Transdermal Electrical Stimulation Devices for Modifying or Inducing Cognitive State [online].[publ. 12.01.2016] The Patent Reader ©2016 Noah K. Tilton [retr. 29.11.2016]. Available online at: https://patents.tilton.co/detail/GMUtility/2016-01-12/09233244</ref>. The Chinese Utility Model Patent No. ZL201320760967.0.<ref name="patent">THYNC.COM: Patent [online]. Copyright ©2016 Thync Global Inc., U.S.A. [retr. 29.11.2016]. Available online at: http://www.thync.com/pat</ref> | ||
| − | == Related Technologies, | + | == Related Technologies, Projects, or Scientific Research == |
Thync has already conducted studies with hundreds participants and their chief science officer Jamie Tyler is the leading researcher in the neuromodulation (with publications in Nature, PLoS ONE, Neuron and Brain Stimulation). From the perspective of MedTech Boston, their responses were substantially better than those given by many other neurotech companies touting their wares on the convention floor of CES.<ref name="MEDTECH BOSTON"/> | Thync has already conducted studies with hundreds participants and their chief science officer Jamie Tyler is the leading researcher in the neuromodulation (with publications in Nature, PLoS ONE, Neuron and Brain Stimulation). From the perspective of MedTech Boston, their responses were substantially better than those given by many other neurotech companies touting their wares on the convention floor of CES.<ref name="MEDTECH BOSTON"/> | ||
| Line 169: | Line 168: | ||
No further studies about Thync has been carried out by a third parties yet. | No further studies about Thync has been carried out by a third parties yet. | ||
| − | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
| − | |||
[[Category:External Hardware or Software]] | [[Category:External Hardware or Software]] | ||
[[Category:Electronic and Other Devices]] | [[Category:Electronic and Other Devices]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Neurostimulation]] | ||
[[Category:Brain Stimulation]] | [[Category:Brain Stimulation]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Vagus Nerve Stimulation]] | ||
[[Category:Transcranial direct-current stimulation]] | [[Category:Transcranial direct-current stimulation]] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:10, 14 July 2017
| Thync | |
|---|---|

|
|
| Category | Transcranial direct-current stimulation |
| Developer | Thync |
| Announced | October 2014 [1] |
| Released | Developers: October 2014 [1]
Consumers: June 2015 [2] |
| Price | 299 USD [2] |
| Max output | 1010 T 10 mA 0.01 A mA[3] |
| Session duration | 12001,200 s 20 minute s[4] |
| Scalp location | from F8 to Fpz, C7 [5] |
| Weight | 18 g [6] |
| Controls |
smartphone, tablet [6] |
| Data available | good |
| Risk factor | low |
| Medical prescription | no |
| http://www.thync.com/ | |
Thync is a small triangular-shaped head-mounted device that puts on the wearer's head. Headset stimulates and activates nerves. The user can either relax or energize. Brain neurons remain intact, the device releases only electrical impulses. In this way, Thync controls user´s mood.[1]
Thync is wirelessly connected to the smartphone or tablet via Bluetooth (iOS or Android app). Users can control Thync by the official app where they can choose the length of the session. Also, they can adjust the strength of the stimulation there (each program follows a pattern of greater and lesser intensity, with cycles of peaks and valleys, but they can also manually raise or lower the overall strength).[7]
The manufacturer raised for this project $13.000.000 and started from October 2014.[1] From 02.06.2015 is the device already publicly available and its price is 299$ (7 245,37 CZK to the 22.9.2016).[2]
Contents
Main Characteristics
Thync releases the low-level electrical pulses to the nerves in the various regions of brain. The manufacturers claim that by the stimulation of different regions, the change of mood appears. Namely, they claim that human mood is influenced by sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. The former is linked with "fight or flight" response and lead to increase of stress, while the latter is associated with relaxation. They argue that their device could increase the state of engergizing or the state of calmness, through stimulation of different regions of brain.[8]
Thync system has three components: module, strips and app. Module placed on forehead and strips on the back of neck. Thync app controls calm or energy vibes via Bluetooth connecting to the smartphone.[6]
The device is made of polycarbonate. The Strips and Liner are made of medical grade skin adhesives, medical grade conductive adhesives, PET film, proprietary conductive inks (nickel free) and 10K gold plated brass snaps. [6]
The dimension of the device is 1in X 2in X 0.5in (in cm: 2.54 x 5.08 x 1.27). The weight of the device is 18 grams. Thync is compatible with iPhone 5, 5s, 5c, 6 and 6 plus and with iOS 8 and higher. Battery Life is 4 to 6 vibes per charge and charge time takes approximately 2 hours via USB charging cable. Thync is wirelessly connected to the smartphone or tablet via Bluetooth (Bluetooth® 4.0 BLE). The other sensors are the singles colour LEDs that indicate power, charge states and current status. Syncing is manual and syncing range is 30 feet (9.15 m). Operating temperature is -4° to 113° F (-20°C to 45°C) and maximum operating altitude is 40,000 feet (12 200 m). Thync is not water resistant.[6]
With regard to the method, Thync uses neurosignaling to the change of mood. This method based on tDCS and TENS techniques, which means that the small and constant direct current or the small pulses of direct current are delivered through skull.[8]
Purpose
Thync is a wearable device whose main purpose is the change of mood. Users can choose 2 modes: calm or energy. One session takes 15-20 minutes.[4]
Company & People
The Thync company was founded by Isy Goldwasser and Jamie Tyler in 2011 in Los Gatos, California. Their team is composed of these people:[9]
- Isy Goldwasser: CEO and Founder
- Jamie Tyler Ph.D.: CSO and Founder (in March 2016 he was substituted for Sumon Pal)
- Sumon Pal Ph.D.: Chief of Vibes
- Anil Thakur: CTO
- Jason Egnal: VP, Digital Marketing & Commercial Operations
Important Dates
- 2011: Co-founding of Company Thync by experts in the fields of neurobiology, neuroscience and consumer electronics from institutions that include MIT, Harvard, and Stanford Universities.[9]
- October 2014: Beginning of the project Thync.[9]
- June 2015: Start selling the device Thync.[9]
- March 2016: The company was experiencing the crisis and reduced his staff.[10]
- April 2016: The company put all of its assets up for auction, fortunately, Thync gained a new investor and therefore it was able to buy up its assets back.[10]
- May 2016: The business has been moving forward.[10]
Enhancement/Therapy/Treatment
In addition to the changes mood, it is deemed that it could help with sleep problems, reduce stress or the motivation to exercise. The manufacturers also believe that the people could reduce consumption of coffee, alcohol and drugs, as a result of introduction this device[11] The Thync company points out that their product Thync is not determined "to treat or diagnose any disease or medical condition".[6]
Ethical Issues
At the conferences that were summarizing named "Introduction to Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation in Neuropsychiatric Research" (2015) and that organized Harvard Medical School[12] were some ethical issues discussed. Alvaro Pascual-Leone criticized that the neurostimulation is using as off-label application and without examination or a full understanding of safety and efficacy implications.[13] Erik Parens focused on the non-physical harms. That means, "how a technology might do harm not to our bodies, but to us as human beings." He distinguishes 4 major concerns: inauthenticity, complicity, mechanization and inequality. Parens also criticizes that "the distinction between treatment and enhancement is abstract and fuzzy".[14] Martha Farah pointed to 4 overlapping categories: safety, efficacy, freedom and fairness.[13] Furthermore, at the conference discussed the following topics: the distinction between treatment and enhancement, necessity of the further study of the long-term safety of neurostimulation, the impact of neurostimulation on the developing brain and the approval by FDA.[13]
In the other study that was named "An ethical discussion of the use of transcranial direct current stimulation for cognitive enhancement in healthy individuals: a fictional case study" and that took place from the January till June 2014 in Rio de Janeiro, these ethical questions emerged:[15]
"(1) whether the modulation of "inner-self" characteristics, such as personality, impulsivity, and social behavior, is acceptable"
"(2) whether tDCS-induced cognitive enhancement is valid as an adjuvant, fair technique for educational purposes or should be considered "cheating" "
"(3) the consequences of the widespread use of neuromodulation for those who either cannot afford it or are not willing to receive it"
"(4) the safety aspects of tDCS"
Health Risks
According to the company, there have been no significant issues regarding Thync’s safety profile. It's known that many people engage in alcohol, drugs, and other activities due to stress, anxiety, and mood problems. Thync may allow for a safer way to alleviate these problems.[16]
Thync also commented safety of their products on their websites. They consider the Thync system as a safe and low-risk transdermal neurostimulation devices. But they also pointed that Thync is not intended to treat or diagnose any disease or medical condition.[8]
As already stated above, the Thync uses TENS and tDCS techniques. Risk of these methods is wrong placement of electrodes. Some people are right-handers, but the others are left-handers. Reversing the polarity can be dangerous and can lead to impairment of brain. At the best, it could mean ineffectiveness, in the worst, headache and brain disorders.[17] The manufacturers of this device recommend that people suffering to Reflex Syncope should consult with their physician before purchasing a Thync System.”[8]
Thync company released on their website "Warnings, Precautions and Adverse Reaction"[6] too.
Public & Media Impact and Presentation
Apart from the fact, that the Thync company has its own website, Facebook, Twitter and Youtube channel, there are the another web portals talking about Thync.
Some people don´t believe that Thync works:
"If this works, it's just a placebo effect." (Amazon, verified purchase, by Eric on September 6, 2015)[18]
"No noticeable effects with Thync." (Amazon, by Alex on August 31, 2015)[18]
"Wishful thinking but didn't work." (Amazon, by EvntHrzn on September 12, 2015)[18]
"I didn’t feel an overwhelming sense of calm or euphoria as was suggested I might. But I did feel a sense of… something due to the device. You definitely feel it working. But it would be hard for me — in a single, short sitting — to say what that was." (PsychCentral, John M. Grohol)[19]
The others claim that Thync really works:
"Really helps me a lot. If you have depression and/or anxiety, give it a try. Company is underselling the benefits." (Amazon, verified purchase, by Fabio on October 24, 2015)[18]
"I rate this 10 stars not five. This product has changed my life in such a positive way." (Amazon, by john m clark on October 7, 2015)[18]
"It's hard for me to say if the placebo effect had any part here. I was told that Thync would make me feel more energetic, and I felt something and did something that enabled the device, and so I suppose it's possible I convinced myself of something. Still, I really believe that the tingles made me feel differently afterward, more alert and tuned-in." (the Daily Dot, Molly McHugh)[20]
"Does it actually work? Yes, for me Thync really did alter the way I felt. Of course, my declaration that it works is based only on my use and the anecdotal experience from the few other people who tried my Thync module."[21]
One customer of Amazon complained about the low battery life:
"It works...but battery life is terrible and support nonexistent so far." (verified purchase, by Seth B on September 15, 2015)[18]
It also appears the cases of burning sensation, pain or headache:
"Indeed, Thync didn’t work for me initially. Instead of a “vibe”, I felt a painful burning sensation and soon gave up. [...] The next day, eager to try again, I positioned the module the way I had been shown. But the burning sensation was back." (Natalia Salmanowitz)[22]
"Today I tried the device at a thync sponsored event. Others claimed to get an effect but to me it mas either not noticeable or like a mild headache. It also seemed to be tricky to set up. I would never buy one." (Amazon, by Carbon Doggie on October 6, 2015)[18]
More detailed reviews are available for viewing below:
Andy Boxall assumed that he felt the effects of Thyncs. But he notes that "there’s a chance it won’t work for others."[21] According to Thync, 80 percent of people will feel the effects. The next disadvantage are the ongoing costs. By them are meant the straps, which should be used only single time. A one pack (5 straps) costs 20$. If someone had used Thync every day, he would spent more than 80$ per month.[21]
John M. Grohol, a psychologist, researcher and expert in mental health, is neutral about Thync. He tried Thync and described that felt an odd sensation but it wasn´t the sensation of calm. He wrote literally: "I didn’t feel an overwhelming sense of calm or euphoria as was suggested I might. But I did feel a sense of… something due to the device. You definitely feel it working. But it would be hard for me — in a single, short sitting — to say what that was."[19]
Natalie Salmanowitz has taken part in a Thync social event at the company’s offices at Runway Incubator. First, she felt the desired energy sensation. She said: "I am not an introvert, but I am also not a small talk enthusiast. Yet, from then on, I was hyper, extroverted, confident and mentally on point. Seems I was vibing."Next day, she tried Thync at home and she felt a pain. About her experience, she speaks as follows: "The next day, I positioned the module the way I had been shown, and tapped start. I felt a familiar feeling, but not the pulsing buzz. Instead, the uncomfortable burning sensation was back. I tried dialling down the intensity and attaching new strips, but the pain persisted."[22] She called by video chat with the support's team because of positioning process but the burning sensation was persisting. Natalia has visited the Thync's headquarters in Los Gatos. Thync's assistant had placed the module on her head but the burning sensation came back. Eventually, Thync's assistant confused that Natalie "deviated from the norm" and her skin was too sensitive for Thync. Another colleague uttered his speculation: "The vibes depend on your current environment" in other words, may mean the placebo effect.[22]
Kyle Russell speaks about his experience with Thync on TechCrunch. He tried only the calm mode but he was satisfied with it: "While I was warned that Thync might not work the first time, a few minutes into my first session (using the Calm setting) I felt a wave of sluggishness pass over me. I had some difficulty putting words into a coherent question for Goldwasser, and felt a strong urge to take a nap that lasted until I got home. While I may have cranked the settings too high for my first go, the impression I got was that it would be great for falling asleep, not de-stressing at the office."[11]
James Trew also described his experience on the web Engadget. He and his colleague Dan Cooper tried Thync at the same point and in the same hotel suit in Las Vegas. There are with them two neuroscientists of Thync (their names wasn't published). Each one of both felt different feeling because the one tried the calm mode and the other tried the energy mode. He only complained of it that the team of Thync has given no scientific explanation of neurosignaling method: "All I know for sure is that I enjoyed my experience. I liked it, and want to try it again. I don't know if this was placebo, a willingness for it to work or something else. I'm definitely not a morning person, and I left the briefing in a very different state to when I went in. I only wish the team were more explicit about the science, the stuff that's going on inside, and allowed us to reveal more about the product. Especially given the natural suspicion that many consumers have about "mood enhancing" devices, and even more so when they're propped up by incomplete insight into what's going on. Now that the energized feeling has faded, I'm left a little frustrated. Something only Thync can solve."[23]
According to Bloomberg, Thync was in crisis in March 2016 because it couldn't get a new investor. Therefore, the company reduced the number of employees and sold its assets: "By March, with a staff of about 10, Thync put all of its assets, including equipment, product inventory, and patents for its electrical and ultrasound brain-stimulation techniques, up for auction. Thync scheduled the event for April 12, according to an e-mail obtained by Bloomberg." Finally, Thync managed to get a new investor and could buy up its assets back. From May 2016, the business has been moving forward.[10]
Public Policy
The CES technique (cranial electrotherapy stimulation) has been approved by FDA to treat the depression, anxiety and insomnia. But the tDCS technique which uses the devices like Thync still isn´t approved by FDA. Thync isn't approved by the Food and Drug Administration because of exempt from medical-device regulation. Geoffrey A. Fowler, the author of this article in The Wall Street Journal, reviewed a letter it sent Thync in which was written that FDA "would consider it a nonmedical “recreational” device as long as it doesn’t change the amount of electrical current it applies, among other factors." [24] The Thync company has put up on their website a decision of FDA too: "The low-risk electrical impulses that Thync uses are so minimal that the product is not subject to medical device regulations by the FDA."[25]
The Thync neurosignaling product is protected by these patents: U.S. Patents 8,903,494[26]; US 9,002,458[27]; US 9,014,811[28]; and US 9,233,244[29]. The Chinese Utility Model Patent No. ZL201320760967.0.[30]
Related Technologies, Projects, or Scientific Research
Thync has already conducted studies with hundreds participants and their chief science officer Jamie Tyler is the leading researcher in the neuromodulation (with publications in Nature, PLoS ONE, Neuron and Brain Stimulation). From the perspective of MedTech Boston, their responses were substantially better than those given by many other neurotech companies touting their wares on the convention floor of CES.[16]
The company Thync published 3 studies that are concerned with their product:
- BOASSO, Alyssa M., et al. Transdermal electrical neuromodulation of the trigeminal sensory nuclear complex improves sleep quality and mood bioRxiv 043901 (2016).
- PANERI, Bhascar, et al. The tolerability of transcranial electrical stimulation used across extended periods in a naturalistic context by healthy individuals PeerJ PrePrints 3:e1341 (2015).
- TYLER, William J., et al. Transdermal neuromodulation of noradrenergic activity suppresses psychophysiological and biochemical stress responses in humans Sci. Rep. 5, 13865 (2015).
No further studies about Thync has been carried out by a third parties yet.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 ADHIKARI, Richard. TECHNEWSWORLD. Thync Scores $13M for Foggy Brain Project[online]. Copyright 1998-2016 ECT News Network. [retr. 22.09.2016]. Available online at: http://www.technewsworld.com/story/81165.html
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 THYNC.COM. Thync Launches First Wearable to Shift Your State of Mind [online]. Copyright 2016 Thync [retr. 22.09.2016]. Available online at: http://www.thync.com/resources/press-release/thync-launches-first-wearable-to-shift-your-state-of-mind
- ↑ PATENTSCOPE. Patent US2013071916-Wearable transdermal electrical stimulation devices and methods of using them[online]. Patentscope, 2014 [retr. 19.10.2016]. Available online at: https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=WO2014082064&recNum=1&maxRec=&office=&prevFilter=&sortOption=&queryString=&tab=PCTDescription
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 THYNC.COM. You Asked, We Answered: Frequently Asked Questions [online]. © Thync 2016 [retr. 18.10.2016]. Available online at: http://www.thync.com/blog/frequently-asked-questions
- ↑ PANERI, Bhascar. The tolerability of transcranial electrical stimulation used across extended periods in a naturalistic context by healthy individuals. [online]. New York : The City College of New York, 2015. [retr. 10.12.2015]. Available online at: http://cdn2.hubspot.net/hubfs/432410/documents/peerJ.pdf?t=1447979598033
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 THYNC.COM. Products [online]. Copyright 2016 Thync [retr. 23.09.2016]. Available online at: http://www.thync.com/products
- ↑ SHANKLIN, Will. Thync mood-changing wearable officially launches - we go hands on (again) [online]. [publ. 02.06.2015] All content copyright © Gizmag 2003 - 2015 [retr. 16.10.2015]. Available online at: http://www.gizmag.com/thync-hands-on-2/37820/
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 THYNC.COM. Science/Technology [online]. Copyright 2015 Thync [retr. 20.10.2015]. Available online at: http://www.thync.com/science-and-technology
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 THYNC.COM. About Us [online]. Copyright 2015 Thync [retr. 16.10.2015]. Available online at: http://www.thync.com/about
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 HUET, Ellen. How Thync, Startup Behind Brain-Zapping Gadget, Almost Died [online]. [publ. 22.05.2016] ©2016 Bloomberg L.P. [retr. 29.11.2016]. Available online at: https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2016-05-23/how-thync-startup-behind-brain-zapping-gadget-almost-died
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 RUSSELL, Kyle. Hands-On With Thync's Mood-Altering Headset [online]. [publ. 02.06.2015] TechCrunch. © 2013-2016 AOL Inc. [retr. 29.11.2016]. Available online at: https://techcrunch.com/2015/06/02/hands-on-with-thyncs-mood-altering-headset/#.jihnn2:JNRc
- ↑ HARVARD MEDICAL SCHOOL. Introduction to Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation in Neuropsychiatric Research [online]. Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, MA 02215, 2015 [retr. 9.11.2016]. Online available at: http://www.hms-cme.net/106409/
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 BAIN, Lisa. NORRIS, Sheena Posey. STROUND, Clare; Rapporteurs. Non-Invasive Neuromodulation of the Central Nervous System: Opportunities and Challenges [online]. United States : Forum on Neuroscience and Nervous System Disorders; Board on Health Sciences Policy; Institute of Medicine; The National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, 2015 (Summary Workshop). [retr. 20.10.2016]. ISBN 978-0-309-37618-1. Available online at: http://www.burke.org/docs/Research_Nina/iom-non-invasive-neuromodulation-ws.PDF
- ↑ PARENS, E. Why IOM Should Consider Broaching ‘Enhancement Concerns’ in the Context of Non-Invasive Brain Stimulation [online]. In Non-invasive Neuromodulation of the Central Nervous System: A Workshop. Washington DC : Institute of Medicine, of the National Academy of Sciences, March 3, 2015. [retr. 9.11.2016]. Available online at: https://www.nationalacademies.org/hmd/~/media/Files/Activity%20Files/Research/NeuroForum/2015-MAR-2/Presentations/Parens.pdf
- ↑ LAPENTA, Olivia M. VALASEK, Claudia A. BRUNONI, André R. BOGGIO, Paulo S. An ethical discussion of the use of transcranial direct current stimulation for cognitive enhancement in healthy individuals: a fictional case study [online]. Psychol. Neurosci. vol.7 no.2 Rio de Janeiro Jan./June 2014. [retr. 24.10.2016]. ISSN 1983-3288. Available online at: http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1983-32882014000200014
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 VAHABZADEH, Arshya. CHAN, Steven. Testing Thync: A Calming, Energizing Personal Brain Modulator [online]. [publ. 12.05.2015] Medtech ©2013-2016 Medical Networking, Inc. [retr. 8.11.2015]. Available online at: https://medtechboston.medstro.com/testing-thync-a-calming-energizing-personal-brain-modulator/
- ↑ MASLEN, Hannah. DOUGLAS, Thomas. KADOSH, Roi Cohen. LEVY, Neil. SAVULESCU, Julian. Mind Machines. University of Oxford, 2014. [retr. 10.12.2015]. Available online at: http://www.oxfordmartin.ox.ac.uk/downloads/briefings/Mind_Machines.pdf.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 18.2 18.3 18.4 18.5 18.6 AMAZON.COM. Customer Reviews: Thync Calm and Energy Wearable , Limited Edition [online]. © 1996-2016, Amazon.com, Inc. [retr. 20.10.2016]. Available online at: https://www.amazon.com/Thync-Calm-Energy-Wearable-Limited/product-reviews/B011EVQBG0/ref=cm_cr_arp_d_viewpnt_lft?ie=UTF8&reviewerType=all_reviews&showViewpoints=1&sortBy=helpful&filterByStar=positive&pageNumber=1
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 GROHOL, J. What Thync Looks & Feels Like. In Psych Central. Copyright © 1995-2016 Psych Central [retr. 19.10.2016]. Available online at: http://psychcentral.com/blog/archives/2015/06/02/what-thync-looks-feels-like/
- ↑ MCHUGH, Molly. Heads-on with Thync, the device that changes your brain [online]. [upd. 12.11.2015] The Daily Dot [retr. 29.11.2016]. Available online at: http://www.dailydot.com/debug/hands-on-thync-ces/
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 21.2 BOXALL, Andy. Thync Review [online]. [upd. 25.10.2016] Digital Trends, 2016 [retr. 19.10.2016]. Available online at: http://www.digitaltrends.com/fitness-apparel-reviews/thync-review/
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 22.2 SALMANOWITZ, Natalie. Thync piece: Do mind-altering wearables live up to the billing? [online]. In New Scientist [publ. 16.4.2016] and [retr. 19.10.2016]. Available online at: https://www.newscientist.com/article/2083126-thync-piece-do-mind-altering-wearables-live-up-to-the-billing/
- ↑ TREW, James. Thync's mood-changing wearable made me happy and frustrated [online]. [publ. 01.07.2015] Engadget. © 2016 AOL TECH(UK). [retr. 29.11.2016]. Available online at: https://www.engadget.com/2015/01/07/thync-mood-changing-wearable/
- ↑ FOWLER, Geoffrey A. This Gadget Gives You a Low Voltage-Voltage Pick-Me-Up-WSJ [online]. [publ. 21.07.2015] The Wall Street Journal. Copyright ©2016 Dow Jones & Company, Inc. [retr. 18.10.2016]. Available online at: http://www.wsj.com/articles/this-gadget-gives-you-a-low-voltage-pick-me-up-1437503825
- ↑ THYNC.COM. How It Works: Low Risk [online]. Copyright ©2016 Thync Global Inc., U.S.A. [retr. 14.11.2016]. Available online at: https://www.thync.com/how-it-works
- ↑ GOLDWASSER, Isy and others. US 8,903,494 B2: Wearable Transdermal Electrical Stimulation Devices and Method of Using Them [online]. [publ. 02.12.2014] The Patent Reader ©2016 Noah K. Tilton [retr. 29.11.2016]. Available online at: https://patents.tilton.co/detail/ElecUtility/2014-12-02/08903494
- ↑ PAL, Sumon K. and others. US 9,002,458 B2: Transdermal Electrical Stimulation Devices for Modifying or Inducing Cognitive State [online]. [publ. 07.04.2015] The Patent Reader ©2016 Noah K. Tilton [retr. 29.11.2016]. Available online at: https://patents.tilton.co/detail/ElecUtility/2015-04-07/09002458
- ↑ PAL, Sumon K. and others. US 9,014,811 B2: Transdermal Electrical Stimulation Methods for Modifying or Inducing Cognitive State [online]. [publ. 21.04.2015] The Patent Reader ©2016 Noah K. Tilton [retr. 29.11.2016]. Available online at: https://patents.tilton.co/detail/ElecUtility/2015-04-21/09014811
- ↑ PAL, Sumon K. and others. US 9,233,244 B2: Transdermal Electrical Stimulation Devices for Modifying or Inducing Cognitive State [online].[publ. 12.01.2016] The Patent Reader ©2016 Noah K. Tilton [retr. 29.11.2016]. Available online at: https://patents.tilton.co/detail/GMUtility/2016-01-12/09233244
- ↑ THYNC.COM: Patent [online]. Copyright ©2016 Thync Global Inc., U.S.A. [retr. 29.11.2016]. Available online at: http://www.thync.com/pat